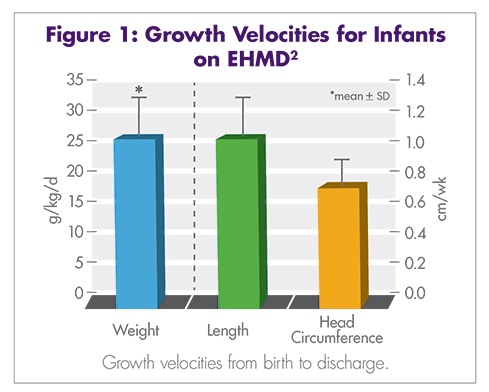
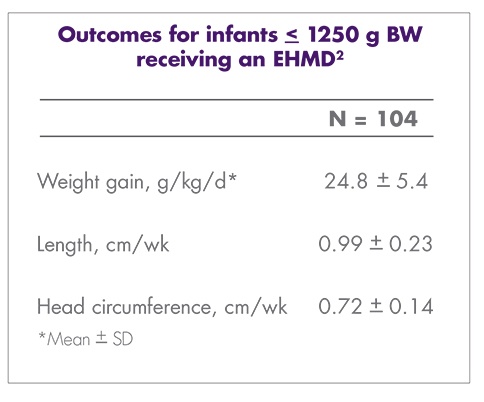
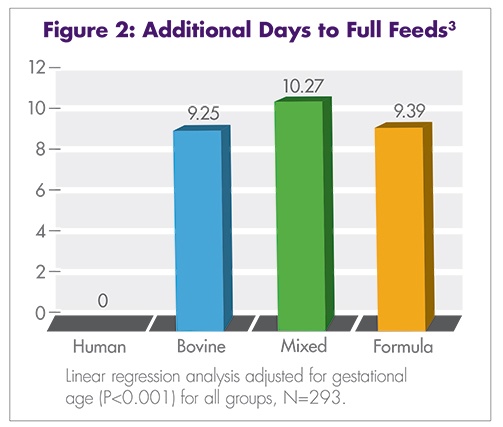
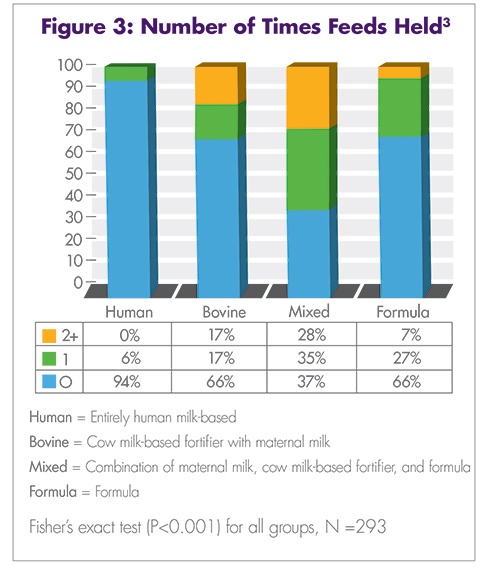
Premature infants have significant nutritional requirements. Increased calories, protein, calcium, and other minerals are vital to their survival, growth, and development. During the last trimester, unborn babies receive vast amounts of nutrition through the umbilical cord. Very premature infants miss this crucial nutrition, and their dietary needs are greater than what breast milk alone can supply. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and the European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) Committee on Nutrition recommend fortifying mother’s milk or pasteurized donor human milk with protein, minerals, and vitamins to ensure optimal nutrition intake and energy intake for premature infants weighing less than 1500 g and less than 1800 g, respectively.1,8
Exclusive Human Milk Diet (EHMD)
An exclusive human milk diet is achieved when 100% of protein, fat, and carbohydrates are derived from human milk. This diet includes:
- Mother’s own milk (MOM) preferred
- Donor human milk
- Human milk-based human milk fortifiers